You might ask what the right glutathione dosage is and if it is safe for you. Research shows that taking oral liposomal glutathione from 250 mg to 1000 mg each day can raise your body’s natural levels by about 30% in a few weeks or months. Many people use glutathione to help their immune system or deal with health problems. You should always talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement to make sure it is safe for you.
Key Takeaways
Glutathione is a strong antioxidant. It protects your cells. It helps your immune system. It helps your body get rid of toxins.
Taking 250 to 1000 mg of oral liposomal glutathione each day can safely raise your glutathione levels. But you should always ask your doctor first.
Glutathione may help your liver. It can make your skin brighter. It may help with some health problems like infertility. It can also help with side effects from chemotherapy.
Some foods help your body make glutathione. These foods are broccoli, eggs, and avocados. Eating these foods can lower the need for supplements.
Do not use inhaled glutathione if you have asthma. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should talk to a doctor before using it. Mild side effects can happen but usually go away fast.
What Is Glutathione?
Role in the Body
Glutathione is called the master antioxidant in your body. Every cell makes it. It is a small molecule built from three amino acids: glutamate, cysteine, and glycine. Its shape lets it fight oxidative stress. When free radicals hurt your cells, glutathione helps protect them. This keeps your cells healthy and slows aging.
Your body needs glutathione for many things:
It protects your cells from oxidative stress by stopping free radicals.
It helps your body get rid of toxins and waste.
It helps your immune system fight off infections.
It helps your cells grow and fix themselves.
When you exercise or get sick, your body uses more glutathione. If you do not have enough, you might feel tired or get sick easier. Scientists found that glutathione also controls signals in your cells. These signals help your body handle stress and heal after getting hurt.
Tip: Doing regular exercise can help your body make more glutathione and recover from oxidative stress faster.
Natural Sources
You can raise your glutathione by eating certain foods. Foods with sulfur amino acids are best. These are lean meats, fish, eggs, beans, nuts, and seeds. Vegetables like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage are also good. Avocados, asparagus, and okra have a lot of glutathione too.
| Food Source | Benefit for Glutathione |
| Broccoli | High in precursors |
| Avocado | Direct glutathione |
| Salmon | Omega-3 support |
| Eggs | Sulfur amino acids |
| Green tea | Antioxidant support |
Cooking food at high heat can lower glutathione, so try to steam or eat them raw. You can also help your body’s glutathione by sleeping well, exercising, and staying away from toxins. Some people use supplements like N-acetylcysteine or alpha-lipoic acid to help their bodies make more glutathione, especially if they have a lot of oxidative stress.
Glutathione Dosage
General Health Dosage
Some people take glutathione to stay healthy. Doctors often tell you to use 250 mg twice a day or 500 mg once a day. These amounts are what many studies use. Some research says 250 mg per day is not better than a sugar pill. Higher doses like 500 mg may work better. IV glutathione is usually given at 1200 mg once a week. Your doctor might change your dose if you need it.
You can get glutathione in different ways:
Oral tablets or capsules: 250–1000 mg each day
IV infusions: up to 1200 mg per session, usually once a week
Intramuscular (IM) injections: 600 mg every other day for some health problems
Inhaled (nebulizer): 600 mg two times a day, but not safe for people with asthma
Note: Always ask your doctor before you start any new supplement. The best dose for you depends on your age, health, and needs.
Skin Dosage
Many people use glutathione to help their skin look lighter or healthier. Studies show that taking 500 mg by mouth each day for four weeks can make skin lighter. Higher doses, like 1000 mg per day, can raise glutathione by up to 35% in six months. Some people start with 1000–2000 mg daily for three months, then use 500 mg daily to keep the results.
| Study Type | Dosage (mg/day) | Duration | Sample Size | Outcome Summary |
| Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | 500 | 4 weeks | 60 | Lower melanin at many skin sites; well tolerated. |
| Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | 250 and 1000 | 6 months | 54 | Higher dose increased glutathione by 30-35%; lower dose by 17%. |
| Open-label study (lozenges) | N/A | N/A | N/A | Improved skin melanin index; buccal route may help absorption. |
| IV administration (no clinical trial) | 600–1200 | Weekly | N/A | Manufacturer recommended; no clinical trial proof for safety and efficacy. |
IV glutathione for skin lightening does not have strong proof from studies. Taking it by mouth is safer, but it may take longer to see changes.
Liver Dosage
Doctors sometimes give glutathione to help people with liver problems. Studies show that 300 mg each day for four months can lower liver swelling. Higher doses, like 500–1000 mg daily, may help protect liver cells and help detox. IV glutathione can be 600 to 2000 mg per session for more serious cases. This way, your body gets almost all of the glutathione. Taking it by mouth only gives about 10–20%.
| Clinical Outcome / Finding | Details / Dosage Information |
| ALT Reduction | 300 mg daily for 4 months lowered liver inflammation. |
| Liver Fat Reduction | Less liver fat seen on scans. |
| Lipid Metabolism Improvement | Lower triglycerides and fatty acids. |
| Ferritin Reduction | Lower ferritin, less oxidative stress. |
| Patient Response Factors | Better results in people with lower blood sugar and higher HDL. |
| Dosage Individualization | Lower daily doses for maintenance; higher or IV doses for detox under doctor care. |
| Safety and Side Effects | Mild side effects possible; check liver enzymes during use. |
| Administration Recommendations | Start slow and use small, steady doses for best safety and efficacy. |
Your doctor should check your liver enzymes if you use glutathione for your liver.
Cancer Dosage
Doctors sometimes use glutathione to help people during cancer treatment. There is no set dose for cancer. Some studies use up to 6000 mg per day, but most use less. Doctors may give glutathione by IV, by mouth, or as a suppository. IV glutathione can help with nerve pain from chemotherapy. Only use glutathione for cancer if your doctor says it is okay because it can mix with cancer drugs.
No set dose for cancer support.
Some plans use up to 6000 mg per day.
IV, oral, and rectal forms are used.
IV glutathione may help with side effects from chemotherapy.
Always use with a doctor’s help.
Safety Limits
It is important to know the safe amount of glutathione. Most studies use 250 to 1000 mg by mouth each day. Some people use up to 2000 mg per day, but using more for a long time is not safe. IV glutathione is usually 10–20 mg for each kg of body weight. IM shots use 600 mg every other day. Inhaled glutathione is 600 mg two times a day, but it can cause asthma attacks.
| Administration Route | Recommended Dosage Range | Notes |
| Oral | 500–2000 mg per day | Split doses; liposomal or sublingual forms may work better |
| IV | 10–20 mg/kg body weight | Example: 1.5 g/m2 before chemotherapy |
| IM | 600 mg every other day | Used in some cancer and infertility protocols |
| Inhaled | 600 mg twice daily | Not safe for asthma; can cause bronchospasm |
| Administration Route | Dosage Examples | Side Effects / Warnings |
| Oral | 50–600 mg/day; 250 mg once daily | Stomach cramps, nausea, bloating |
| IM | 600 mg/day or every other day | Allergic reactions, low zinc levels |
| IV | 1.5 g/m2 before chemotherapy | Not enough safety data for high doses |
| Inhaled | 600 mg twice daily | Asthma risk; avoid if you have asthma |
⚠️ Caution: Do not use inhaled glutathione if you have asthma. Using it for a long time may lower zinc levels. It is not known if glutathione is safe for pregnant or breastfeeding women. Supplements are not checked by the FDA, so always talk to your doctor.
Always follow the dose your doctor tells you and do not take too much. Doctors may change your dose based on your health and goals. How safe and helpful glutathione is depends on the form, dose, and your health. Most people do not have problems with glutathione at the right dose, but you should watch for side effects.
Tip: For best safety, use glutathione for up to two months at a time unless your doctor says you can use it longer.
Medical Uses
Liver Diseases
Glutathione can help your liver stay healthy. Studies show it helps people with liver diseases like NAFLD and alcoholic liver problems. Some patients took glutathione by mouth or got it through a shot. Their liver enzymes went down, and they had less stress in their bodies. One study gave people 300 mg of glutathione each day for four months. Their ALT levels dropped, and they had less fat in their livers. Another study used higher doses by shot for 30 days. These people had better liver tests and less damage from stress. Most people did not have side effects.
Doctors in India use glutathione shots for alcoholic liver disease. The CDSCO in India says this is okay. But most studies are small and do not last long. There are no big phase III studies yet. You should ask your doctor before using glutathione for your liver.
Note: Glutathione might help your liver heal and lower swelling, but more studies are needed to know for sure.
Neurological Disorders
Glutathione is important for your brain. Low glutathione is linked to diseases like Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and multiple sclerosis. People with these diseases often have less glutathione in their brains. This can cause more stress and faster nerve damage.
Some studies say raising glutathione may protect your brain. For example, N-acetyl-cysteine helps your body make more glutathione. It can lower nerve cell damage in Parkinson’s disease. New research shows that putting glutathione in your nose can raise brain levels. This way may help treat brain diseases later.
Doctors and scientists are still learning about glutathione for brain health. They want to find more ways to use it. Clinical trials are still happening, and there are no official rules yet.
Infertility
Glutathione may help some men who cannot have children. One study looked at 20 men with poor sperm. They got 600 mg of glutathione by shot every other day for two months. After one month, their sperm moved better and looked better. But these changes did not last after stopping the shots. The study was small, so more research is needed.
Doctors sometimes use glutathione for men with sperm problems from swelling or varicocele. Ask your doctor if this is right for you. The good effects may not last long, and more studies are needed.
Chemotherapy Support
Doctors sometimes give glutathione to people getting chemotherapy. Chemotherapy can hurt nerves and cause other problems. Glutathione may protect nerves and lower these side effects. In the Philippines, the FDA says glutathione can help lower nerve problems from cisplatin chemotherapy.
Studies show that glutathione shots can help cancer patients feel less nerve pain. Doctors use different amounts and ways to give it, but always watch closely. Never use glutathione during cancer treatment without asking your doctor. Some chemo drugs can mix badly with glutathione, so safety is very important.
Immune and Skin
Glutathione helps your immune system and skin. It is a strong antioxidant that fights stress and helps you get better when sick. Studies show glutathione can raise blood levels, lower swelling, and make older people stronger. One study found people with type 2 diabetes who took 500 mg daily for six months had better blood sugar and immune health.
Glutathione can also help your skin. It can lighten dark spots and make your skin look brighter by blocking melanin. Studies show that taking glutathione by mouth or putting it on your skin can lower melanin and brighten skin. One study in Filipino women found that using a glutathione lotion twice a day for ten weeks made skin lighter with no side effects. Another study showed that glutathione lozenges made skin color better and were safe.
Doctors use glutathione for skin lightening in some places, but the proof is mixed. Shots work faster but can be risky. Pills and creams are safer but take longer to work. Always talk to your doctor before using glutathione for your skin or immune system.
| Medical Use | Clinical Evidence | Regulatory Status | Typical Benefits |
| Liver Diseases | Many studies | Approved in India (IV) | Lower liver enzymes, less fat |
| Neurological Disorders | Ongoing studies | Not FDA approved (US) | May protect brain, reduce stress |
| Infertility | Small trial | Not FDA approved | Improved sperm quality |
| Chemotherapy Support | Clinical trials | Approved in Philippines | Less nerve damage, fewer side effects |
| Immune & Skin | Clinical trials | Not FDA approved (US) | Brighter skin, better immunity |
Tip: Glutathione’s benefits depend on your health, how you use it, and how long you take it. Always ask your doctor before starting any new treatment.
Glutathione Interactions
Drug Interactions
Glutathione can change how your body uses some medicines. It works in your liver to help remove harmful parts from drugs like acetaminophen. This helps keep your cells safe from damage. Some studies show that IV glutathione can lower nerve pain from chemotherapy drugs like cisplatin. Doctors sometimes use it to help people feel better during cancer treatment. There is not much information about how glutathione mixes with other drugs besides chemo and detox. You should always tell your doctor about all the medicines you take before using glutathione.
| Drug or Treatment | Possible Interaction or Effect | Clinical Evidence Source |
| Cisplatin (chemotherapy) | Reduces nerve damage and toxicity | Clinical trials (Leone et al., Smyth et al.) |
| Acetaminophen (overdose) | Helps detoxify harmful metabolites | DrugBank, clinical pharmacology |
| Other chemotherapy agents | May affect drug resistance in cancer cells | O’Brien & Tew, Calvert et al. |
| Inhaled use in asthma | May worsen breathing problems | WebMD, clinical warnings |
Note: Research shows glutathione can change how your body reacts to some drugs, especially during cancer treatment.
Supplement Interactions
You might take other supplements or herbs with glutathione. Curcumin from turmeric can help your body fight stress. Curcumin raises glutathione and helps enzymes work better. This mix may help your body fight swelling and damage. Most reports say glutathione only has mild effects with other supplements. Still, you should talk to your doctor before mixing supplements, especially if you use many at once.
Who Should Avoid
Some people should not use glutathione. If you have asthma, you could have more trouble breathing, especially with inhaled forms. Studies show people with bad asthma have less glutathione in their airways, which can make swelling worse. Kids with asthma also have more airway injury, even with treatment. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, you should not use glutathione because there is not enough safety data. People with strong allergies should be careful, as glutathione could make symptoms worse.
⚠️ Caution: If you have asthma, strong allergies, or are pregnant or breastfeeding, do not use glutathione unless your doctor says it is safe.
Side Effects
Common Effects
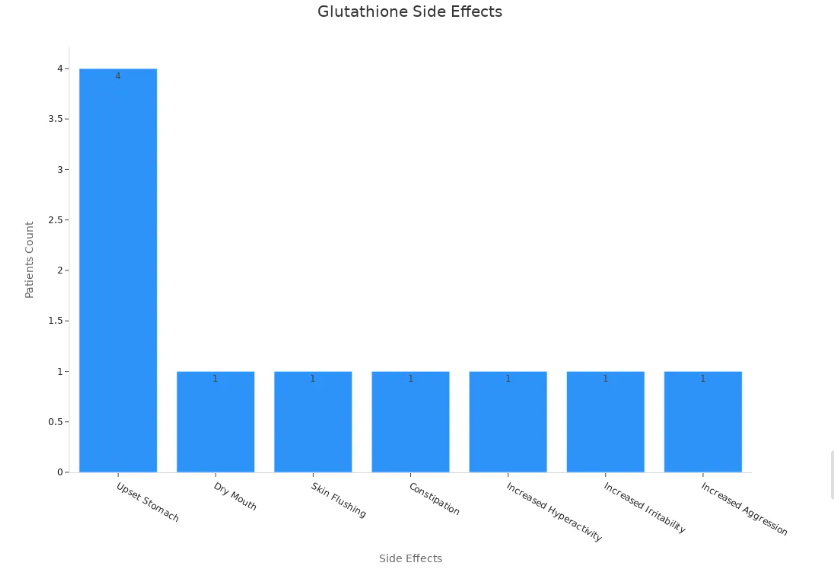
Some people get mild side effects from glutathione. Most people do not have big problems. You might feel sick to your stomach, have a dry mouth, or notice your skin gets red. In one small study, six kids took glutathione by mouth. Four of them had an upset stomach. Other side effects were dry mouth, red skin, constipation, and changes in mood. Some kids felt more hyper or got irritated easily. Only one child stopped taking it because they felt too irritated.
| Side Effect | Number of Patients (n=6) |
| Upset Stomach | 4 |
| Dry Mouth | 1 |
| Skin Flushing | 1 |
| Constipation | 1 |
| Increased Hyperactivity | 1 |
| Increased Irritability | 1 |
| Increased Aggression | 1 |
Most people who use glutathione do not have serious problems. You may only notice mild discomfort that goes away after a short time.
Serious Risks
You might wonder if glutathione is very risky. Studies in animals and people show even high doses are not very harmful. In one study, rats got a lot of a glutathione precursor for 13 weeks. The rats did not get sick or die. Their organs stayed healthy. Human studies also did not find any big risks or changes in health. Doctors have not seen life-threatening side effects in healthy adults.
Precautions
You should be careful with any supplement. If you have asthma, do not use inhaled glutathione. It can make breathing harder. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not use glutathione unless a doctor says it is okay. If you get new symptoms like trouble breathing, swelling, or a rash, stop using it and call your doctor. Always listen to your doctor about how much to take and watch for any changes in how you feel.
Tip: Try a small amount first to see how your body feels. This can help you avoid unwanted side effects from glutathione.
Supplementation
Dietary Sources
You can help your body make more glutathione by eating certain foods. Foods with a lot of sulfur, like beef, fish, and eggs, give your body what it needs. Broccoli and kale are vegetables that also help your body make glutathione. Garlic and onions add even more sulfur to your meals. Spinach, avocados, asparagus, and okra have glutathione, but your body does not take in much from food.
Vitamin C is important for keeping glutathione working in your body. It acts as an antioxidant and helps your cells use glutathione again. Studies show that taking vitamin C can raise glutathione in your blood by up to half. Whey protein is another good choice. It has cysteine, which your body uses to make glutathione. Research shows people who eat whey protein have more glutathione and less swelling in their bodies.
| Dietary Source | Evidence Type | Summary of Effect on Glutathione Levels |
| Sulfur-rich foods | Human and animal studies | Beef, fish, poultry, cruciferous vegetables, garlic, and onions increase glutathione by reducing oxidative stress. |
| Vitamin C | Clinical trials | Supplementation increased glutathione in white blood cells by 18% and red blood cells by 47%. |
| Selenium-rich foods | Supplementation studies | Selenium acts as a cofactor; supplementation increased glutathione peroxidase in patients with kidney disease. |
| Glutathione-rich foods | Observational studies | Spinach, avocados, asparagus, and okra may reduce oxidative stress, but glutathione is poorly absorbed from food. |
| Whey protein | Multiple clinical studies | Rich in cysteine, shown to increase glutathione levels and reduce oxidative stress. |
Tip: Eating many of these foods helps your body make more glutathione. This may help you not need extra glutathione supplements.
Choosing Supplements
If you want to try glutathione supplements, you should pick the right kind. Not all glutathione supplements work the same. Your body breaks down regular glutathione pills before it can use them. Liposomal glutathione has a special cover that helps your body take in more. Studies show liposomal forms lower stress in your body better than regular pills.
When you buy glutathione supplements, look for these things:
Liposome size smaller than 200 nanometers for better use.
Phospholipids from non-GMO plants, like sunflower lecithin.
The reduced form (L-glutathione) with proof of purity.
Packaging that keeps out light and air to keep it fresh.
Made in cGMP-certified places with good quality checks.
Extra things like vitamin C or selenium to help glutathione work.
Clear storage and dose instructions on the label.
Do not pick just by price. Cheaper glutathione may not work well.
Some glutathione supplements have brand names, like Setria or Opitac. These have been tested and shown to raise glutathione in the blood. Orobuccal forms melt in your mouth and help your body use glutathione faster. Always check for testing and clear labels before you start taking glutathione.
Note: Talk to your doctor before you start any new supplement. Glutathione works best when you pick a good product and use the right amount.
You now know that glutathione can help your health in different ways. Studies show it is good for your liver, helps some men with infertility, and may help with some brain problems. Some research found that it made sperm better, lowered liver test numbers, and raised antioxidant levels. But doctors do not say everyone should use glutathione, and there are not enough big studies yet. Always ask your doctor before you try any new supplement. This way, you can make smart choices and care for your health.
FAQ
What is the safest way to take glutathione?
You can take glutathione as a pill or capsule by mouth. Liposomal types help your body use it better. Always listen to your doctor for the safest way.
How long does it take to see results from glutathione?
You might see changes in your skin or feel more energy in four to six weeks. Some people notice results even sooner. How fast you see changes depends on your body and your health goals.
Who should not use glutathione supplements?
Do not use glutathione if you have asthma, strong allergies, or if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Always talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement.
Can you take glutathione with other vitamins or supplements?
Most people can use glutathione with vitamin C, selenium, or whey protein. These can help glutathione work better. Always ask your doctor before mixing supplements.
What are the most common side effects of glutathione?
| Side Effect | How Often It Happens |
| Upset stomach | Sometimes |
| Dry mouth | Rare |
| Skin flushing | Rare |
Most side effects are mild and do not last long.
















